Title
Content
Title
Content

Ultraviolet (UV) light has been associated with the inactivation of microorganisms for a long time1, but its use in indoor environments is constantly advancing. Here is a closer look at current trends in UV disinfection technology.
UV light is an invisible form of radiation that is part of the electromagnetic spectrum. Its frequencies range between 100 and 400 nanometers (nm) and it occurs naturally in sunlight.2
At certain frequencies, UV light is deemed highly effective as a germicidal disinfectant. These frequencies would be between 200 and 280 nm, and are known as Ultraviolet C, or UV-C light.3

UV-C light is used in the process of ultraviolet germicidal irradiation, or UVGI. At frequencies of 254 nm, UV-C light can be implemented to disinfect liquids, surfaces, and the air.4 5
Typically in indoor environments, UVGI is used to disinfect the air and surfaces of microorganisms such as:
When combined with traditional manual cleaning and disinfection methods, 254 nm UV-C light has been associated with over 99.9% reductions of certain microorganisms.7 8 7
There are certain microorganisms that are frequently found in indoor environments.
These include, but are not limited to:
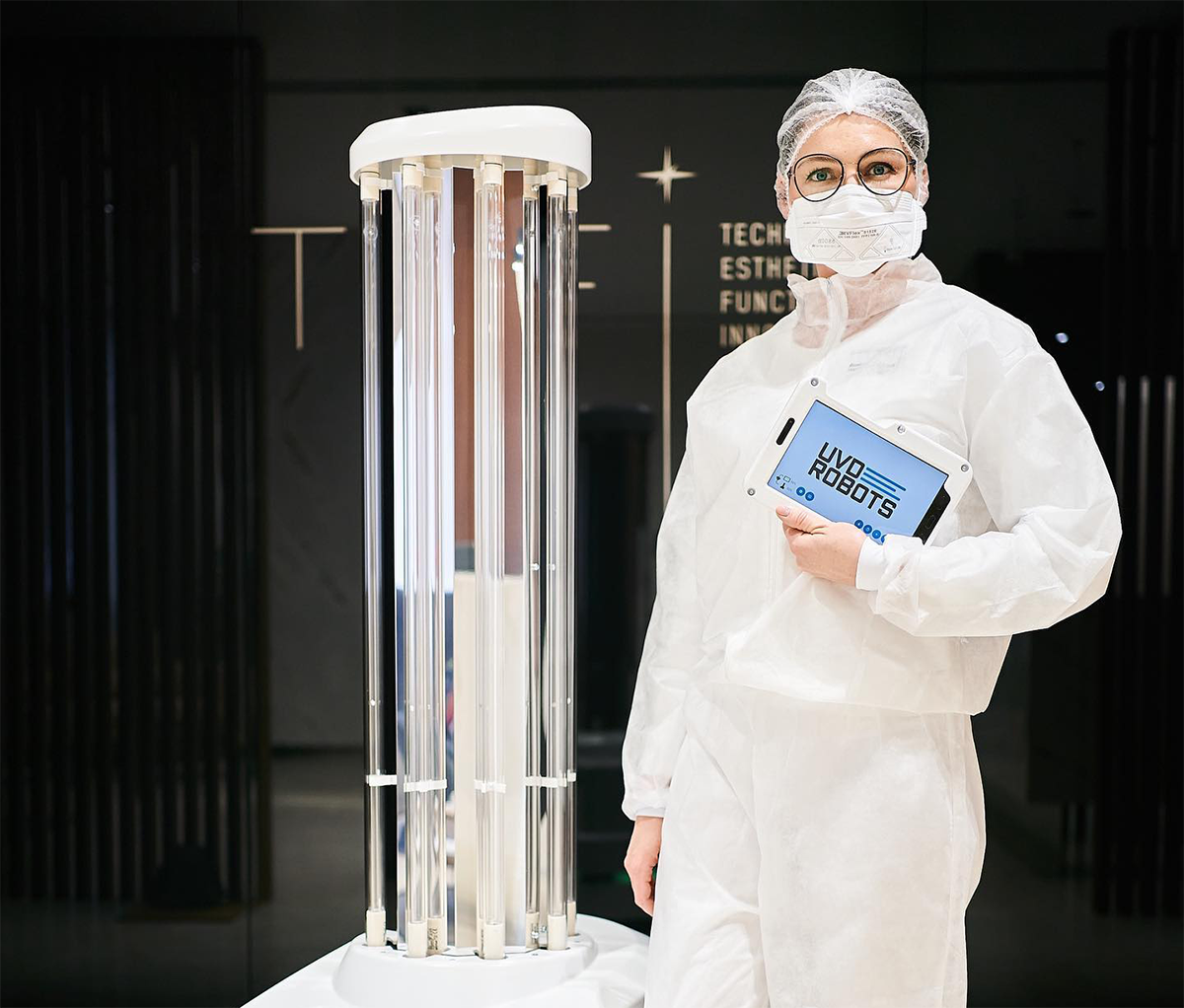
UVD Robots are a series of mobile, self-navigating robots that emit 254 nm UV-C light.12 These robots were pioneered by Blue Ocean Robotics, a Danish company that develops mobile robots for the service industry.

As autonomous units, UVD Robots can operate using a “no-touch” disinfection method that can perform disinfection functions in rooms in a period as short as 10 minutes.13 These robots are used in conjunction with manual cleaning methods to reach maximal efficacy.14
UVD Robots are autonomous disinfection robots that emit 254 nm UV-C light.15 They are a mobile method of UV disinfection that has come to serve indoor environments, with efficacy rates of at least 99.99%.16
1. Downes, Arthur, and Thomas P. Blunt. "IV. On the influence of light upon protoplasm." Proceedings of the Royal Society of London 28.190-195 (1879): 199-212.
2. Illuminating Engineering Society. “IES Committee Report CR-2-20 FAQs.” Illuminating Engineering Society, 7 Mar. 2022, www.ies.org/standards/committee-reports/ies-committee-report-cr-2-20-faqs.
3. Illuminating Engineering Society. “IES Committee Report CR-2-20 FAQs.” Illuminating Engineering Society, 7 Mar. 2022, www.ies.org/standards/committee-reports/ies-committee-report-cr-2-20-faqs.
4. Guillard, Chantal, et al. "Microbiological disinfection of water and air by photocatalysis." Comptes Rendus Chimie 11.1-2 (2008): 107-113
5. Andersen, Helle Stendahl. Analysis Report: Test of UV Disinfection Robot acc. NF T72-281. Report Number 754372_Rev. 2. Danish Technological Institute, 2020
6. Kowalski, Wladyslaw. Ultraviolet germicidal irradiation handbook: UVGI for air and surface disinfection. Springer science & business media, 2010.
7. Edwards-Jones, Val. "Assessment of UVD Robot Against Reduction of MultiDrug Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae, Acinetobacter baumannii and Clostridium difficile on Surfaces." Essential Microbiology Ltd. and Melbec Microbiology Ltd., Apr. 2019, www.melbecmicrobiology.co.uk, www.essentialmicrobiology.com.
8. Andersen, Helle Stendahl. Analysis Report: Test of UV Disinfection Robot acc. NF T72-281. Report Number 754372_Rev. 2. Danish Technological Institute, 2020.
9. Edwards-Jones, Val. "Assessment of UVD Robot Against Reduction of MultiDrug Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae, Acinetobacter baumannii and Clostridium difficile on Surfaces." Essential Microbiology Ltd. and Melbec Microbiology Ltd., Apr. 2019, www.melbecmicrobiology.co.uk, www.essentialmicrobiology.com.
10. Andersen, Helle Stendahl. Analysis Report: Test of UV Disinfection Robot acc. NF T72-281. Report Number 754372_Rev. 2. Danish Technological Institute, 2020
11. "Annex 3 - Logarithmic Reduction.” Food Standards Agency, https://www.food.gov.uk/business-guidance/annex-3-logarithmic-reduction
12. Mehta, Ishaan, et al. "UV disinfection robots: A review." Robotics and Autonomous Systems (2022): 104332.
13. Edel, Dan. “Virus Killing UVD Robots Can Autonomously Disinfect A Room In 10 Minutes.” Intelligent Living, https://www.intelligentliving.co/virus-killing-uvd-robots/.
14. Mehta, Ishaan, et al. "UV disinfection robots: A review." Robotics and Autonomous Systems (2022): 104332.
15. Mehta, Ishaan, et al. "UV disinfection robots: A review." Robotics and Autonomous Systems (2022): 104332.
16. Tuleshov, Amandyk, et al. "Design and construction of a multifunctional disinfection robot." Eastern-European Journal of Enterprise Technologies 1.1 (2022): 115.